Essay
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market, the market supply and demand are:
Supply: P = 30 + 0.50Q
Demand: P = 100 - 1.5Q,
where P is dollars per unit and Q is rate of production and sales in hundreds of units per day. A typical firm in this market has a marginal cost of production expressed as:
MC = 3.0 + 15q.
a. Determine the market equilibrium rate of sales and price.
b. Determine the rate of sales by the typical firm.
c. Determine the economic rent that the typical firm enjoys. (Hint: Note that the marginal cost function is linear.)
d. If an output tax is imposed on ONE firm's output such that the ONE firm has a new marginal cost (including the tax) of: 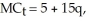 what will the firm's new rate of production be after the tax is imposed? How does this new production rate compare with the pre-tax rate? Is it as expected? Explain. Would the effect have been the same if the tax had been imposed on all firms equally? Explain.
what will the firm's new rate of production be after the tax is imposed? How does this new production rate compare with the pre-tax rate? Is it as expected? Explain. Would the effect have been the same if the tax had been imposed on all firms equally? Explain.
Correct Answer:

Verified
a.The market equilibrium price and sales...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q154: Suppose we plot the total revenue curve
Q155: The textbook for your class was not
Q156: Consider the following statements when answering this
Q157: When the price faced by a competitive
Q158: Bette's Breakfast, a perfectly competitive eatery, sells
Q159: Short-run supply curves for perfectly competitive firms
Q160: Consider a competitive market in which the
Q161: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3095/.jpg" alt=" Figure 8.5.2 -Refer
Q163: If price is between AVC and ATC,
Q164: In long-run competitive equilibrium, a firm that