Multiple Choice
Figure 7-6 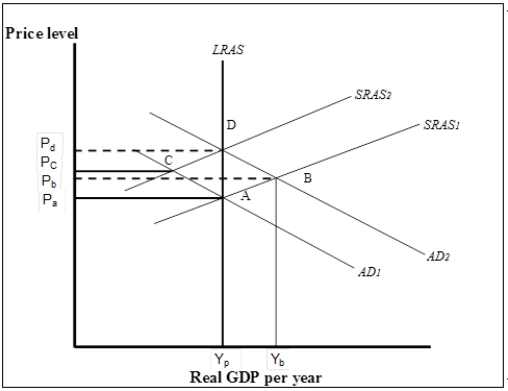
-Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. Policy makers could either pursue a stabilization policy or allow the economy to adjust on its own. What is the difference between the two policy choices, if any?
A) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd.
B) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa.
C) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa.
D) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q62: What happens in the domestic economy when
Q66: Figure 7-3 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5507/.jpg" alt="Figure 7-3
Q67: Figure 7-7 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5507/.jpg" alt="Figure 7-7
Q90: The aggregate demand curve shifts due to
Q91: A change in the price level, all
Q98: A change in the aggregate quantity of
Q99: The rise and fall of real GDP
Q116: The sticky price explanation of the short-run
Q153: The short run in macroeconomic analysis is
Q158: If an economy is operating at its