Multiple Choice
The fluorocarbon 
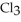
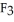 has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C. The specific heats of
has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C. The specific heats of 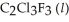 and
and 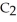
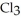
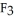 (g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1, respectively. The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1. The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at
(g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1, respectively. The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1. The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at 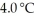 to the gas at 70.0 °C is ________ kJ.
to the gas at 70.0 °C is ________ kJ.
A) 10.07
B) 2742
C) 30.22
D) 9.86
E) 4.60
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q4: Define volatile.
Q64: How many H<sup>-</sup> ions are around each
Q67: Choose the molecule or compound that exhibits
Q69: What is the strongest type of intermolecular
Q70: Why is water an extraordinary substance?<br>A) Water
Q71: The normal boiling point of water is
Q74: Based on the figure above, the boiling
Q75: Choose the substance with the lowest surface
Q92: Which of the following is considered a
Q122: Define freezing.<br>A) the phase transition from solid