Essay
In 1925, David Keilin used a simple spectroscope to observe the characteristic absorption bands of the cytochromes that participate in the electron-transport chain in mitochondria.A spectroscope passes a very bright light through the sample of interest and then through a prism to display the spectrum from red to blue.If molecules in the sample absorb light of particular wavelengths, dark bands will interrupt the colors of the rainbow.His key discovery was that the absorption bands disappeared when oxygen was introduced and then reappeared when the samples became anoxic.Subsequent findings demonstrated that different cytochromes absorb light of different frequencies.When light of a characteristic wavelength shines on a mitochondrial sample, the amount of light absorbed is proportional to the amount of a particular cytochrome present in its reduced form.Thus, spectrophotometric methods can be used to measure how the amounts of reduced cytochromes change over time in response to various treatments.If isolated mitochondria are incubated with a source of electrons such as succinate, but without oxygen, electrons enter the respiratory chain, reducing each of the electron carriers almost completely.When oxygen is then introduced, the carriers oxidize at different rates, as can be seen from the decline in the amount of reduced cytochrome (see Figure 14-27).Note that cytochromes a1 and a3 cannot be distinguished and thus are listed as cytochrome (a1 + a3).How does this result allow you to order the electron carriers in the respiratory chain? What is their order? 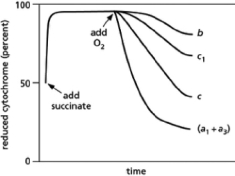
Figure 14-27
Correct Answer:

Verified
This result allows you to order the elec...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q38: Consider a redox reaction between molecules A
Q39: The relationship of free-energy change (ΔG) to
Q40: Explain how scientists used artificial vesicles to
Q41: If you add a compound to illuminated
Q42: For each of the following sentences,
Q44: Cytochrome c oxidase is an enzyme complex
Q45: Bongkrekic acid is an antibiotic that inhibits
Q46: Human infants have a much larger portion
Q47: Name the mitochondrial localization of each of
Q48: During Stage 2 of oxidative phosphorylation, ATP