Multiple Choice
The stability of 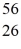 Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known:
Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known: 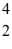 He: 4.002603 u
He: 4.002603 u 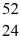 Cr: 51.944768 u
Cr: 51.944768 u 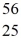 Mn: 55.938907 u
Mn: 55.938907 u 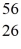 Fe: 55.934939 u
Fe: 55.934939 u 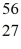 Co: 55.939841 u The
Co: 55.939841 u The  Fe nuclide is
Fe nuclide is
A) not subject to alpha, β+, or β- decay.
B) subject to alpha decay only.
C) subject to β+decay only.
D) subject to β- decay only.
E) subject to β+ or β- decay, but not to alpha decay.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: Radium-226 decays into radon-222 plus an alpha
Q8: The maximum permissible workday dose for occupational
Q9: Consider the short-lived neutral isotope represented by
Q24: A radioisotope has a half-life of τ
Q33: The carbon in your body was formed
Q41: The radioactive nuclei <sup>60</sup>Co is widely used
Q52: Two identical nuclei of mass 18 u
Q53: A radioactive isotope decays by β<sup>-</sup> emission
Q69: A certain nucleus containing 8 protons and
Q73: If a nucleus decays by alpha decay