Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question.
The mechanism of cell crawling in protist species is not well defined. Pseudopodia extension involves interactions between actin and myosin (the same molecules that are involved in vertebrate muscle contraction) . However, prior to the study described below, no one had provided convincing data that actin and myosin were actually involved in cell crawling in protists. Anatomical studies had identified the cytoskeletal protein actin just below the surface of the cell membrane in several species of protist, but physiological studies had failed to show a functional link between actin, myosin, and cell crawling.
In a study by N. Poulsen et al. (Diatom gliding is the result of an actin-myosin motility system, Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 44 (1999) :23-22) , researchers tested whether motility in a particular species of diatom involves interactions between actin and myosin.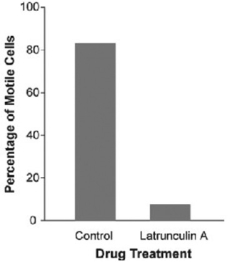
Refer to the study by Poulsen et al. and the figure above. Latrunculin A is a reversible toxin that disrupts the formation of actin fibers. A culture of a particular species of diatom was treated with this toxin diluted in a buffer, while another culture was treated only with the buffer (no toxin; control) . The motility of cells in each culture was assessed by counting the number of cells that were moving during a defined period of time. Which of the following conclusions is reasonable based on the above figure?
A) Formation of actin fibers is not necessary for the movement in this species of diatom.
B) The buffer alone largely inhibited movement in this species of diatom.
C) In this species of diatom, fully formed actin fibers are necessary for movement.
D) In this species of diatom, fully formed myosin proteins are necessary for movement.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q52: Use the following information to answer the
Q53: Predict the most likely outcome of fertilizing
Q54: Use the following information to answer the
Q55: Similar to most amoebozoans, the forams and
Q56: Previously recognized similarities that seemed to connect
Q58: An individual mixotroph loses its plastids, yet
Q59: Use the following information to answer the
Q60: Which of the following is characteristic of
Q61: A gelatinous seaweed that grows in shallow,
Q62: You are given four test tubes, each