Multiple Choice
Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands (M.G.A. van der Heijden, J. N. Klironomos, M. Ursic, P. Moutoglis, R. Streitwolf-Engel, T. Boler, A. Wiemken, and I. R. Sanders. 1998. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and productivity. Nature 396:69-72) . Specifically, they wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A, B, C, and D) , no AMF species (O) , or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D) ; and they measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot, so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species were present.
On the graphs, the x-axis labels indicate the number and identity of AMF species (bar 0 = no fungi; bars A - D = individual AMF species; bar A + B + C + D = all AMF species together) . The y-axis indicates the amount (grams) of plant biomass for the species shown in italics above each graph. Graph e is the total biomass (grams) of all 11 plant species combined; graph f is the biomass of Bromus erectus plants only, separated from the total.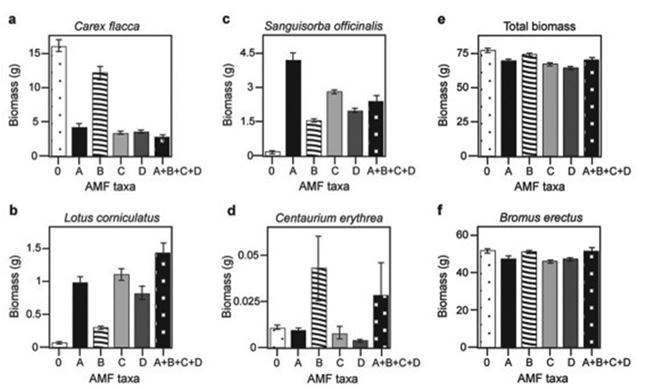
Based on graphs e and f, which is the most well-supported prediction for the effect on total plant biomass if AMF diversity were increased to eight species?
A) No effect is predicted, because the dominant species is unaffected by AMF diversity.
B) Total biomass for eight species would double in comparison to that for four species.
C) Rare species would produce more biomass compared to the case when fewer AMF are present.
D) No effect is predicted, because the dominant species is non-mycorrhizal.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Which of the following best describes the
Q3: Fungi produce many compounds that humans are
Q4: Use the information to answer the following
Q5: What do fungi and arthropods have in
Q6: Which feature seen in chytrids supports the
Q8: Use the following information to answer the
Q9: When a mycelium infiltrates an unexploited source
Q10: The multicellular condition of animals and fungi
Q11: The ascomycete Brachiola gambiae parasitizes the mosquito
Q42: The closest relatives of fungi are thought