Multiple Choice
Figure 17-1 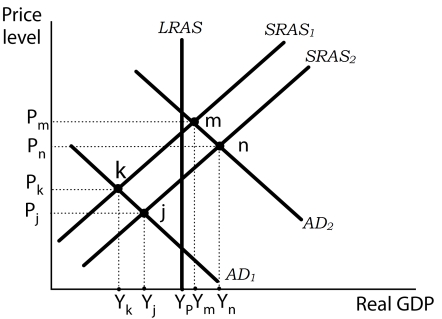
-Refer to Figure 17-1. During the Great Depression, aggregate demand declined sharply. Suppose the economy moved to a short-run equilibrium at point k. Over time, the economy moved to point j. What could have caused the economy to move to point j?
A) Falling output prices caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
B) Falling nominal wages caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
C) Expansionary fiscal policies caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
D) A decline in the demand for U.S. goods by foreign countries aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q25: A policy implication of Keynesian economics is
Q44: Early classical macroeconomics was based largely on
Q62: Figure 17-3 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5507/.jpg" alt="Figure 17-3
Q63: David Ricardo focused on the economy in
Q65: Figure 17-1 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5507/.jpg" alt="Figure 17-1
Q67: One distinguishing feature of new Keynesian economics
Q69: The classical school focused on the long-run
Q84: In the 1960s, despite the successful application
Q89: In the new classical view,<br>A) a change
Q117: Prior to the Great Depression, the dominant