Multiple Choice
The following MINITAB output presents a multiple regression equatior =b0+b1x1+b2x2+b3x3+b4x4
The regression equation is
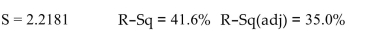
Let be the coefficient Test the hypothesis rersus
level. What do you conclude?
A) Do not H0
B) Reject H0
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q14: Use the given set of points
Q15: The summary statistics for a certain
Q16: In a study of reaction times,
Q17: The following MINITAB output presents a
Q18: The following MINITAB output presents a
Q20: Use the given set of points
Q21: Use the given set of points
Q22: The following table lists values measured
Q23: Use the given set of points
Q24: Use the given set of points