Essay
You are given a 4-stage pipelined processor as described below.
IF: Instruction Fetch
IDE: Instruction Decode, Register Fetch, ALU evaluation, branch instructions change PC, address calculation for memory access.
MEM: memory access for load and store instructions.
WB: Write the execution result back to the register file. The writeback occurs at the 2nd half of the cycle.
Assume the delayed branching method discussed in Section 4.3. For the following program, assume that the loop will iterate 15 times. Assume that the pipeline finishes one instruction every cycle except when a branch is taken or when an interlock takes place. An interlock prevents instructions from being executed in the wrong sequence to preserve original data dependencies. Assume register bypass from both the IDE output and the MEM output. Also assume that r2 will not be needed after the execution returns.
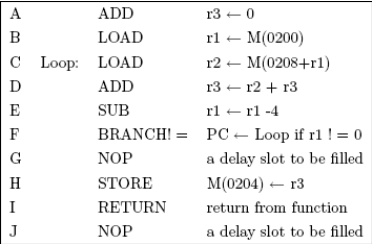 (a) Is there any interlock cycle in the program? If so, perform code reordering on the program and show the new program without interlock cycle.
(a) Is there any interlock cycle in the program? If so, perform code reordering on the program and show the new program without interlock cycle.
(b) Derive the total number of cycles required to execute all instructions before and after you eliminated the interlock cycle.
(c) Fill the delay slots. Describe the code reordering and/or duplication performed. Show the same program after delay slot filling. Recall that RETURN is also a branch instruction. Use a ' to mark the new copy of a duplicated instruction. For example, if you duplicated D, name the new copy D'.
(d)Derive the total number of cycles required to execute all instructions after you filled the delay slots.
Correct Answer:

Verified
a. There is an interlock cycle in the pr...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q6: Consider a MIPS machine with a 5-stage
Q7: Branch Prediction. Consider the following sequence of
Q8: Branch Prediction. Consider the following sequence of
Q9: This problem covers your knowledge of
Q10: Imagine an instruction whose function is to
Q12: This is a three-part question about critical
Q13: Forwarding logic design. For this problem you
Q14: Branch Prediction. Consider the following sequence of
Q15: Pipelining is used because it improves instruction
Q16: This is a three-part question about critical