Multiple Choice
Given that M represents the money supply, i represents interest rates, I represents investment, AD represents aggregate demand, V represents the velocity of money, C represents consumption, P represents the price level, and Q represents the economy's real output level, Friedman's monetarist transmission mechanism can be represented by
A) 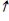 M → (
M → ( i and/or
i and/or C) →
C) →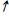 I →
I →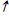 AD →
AD →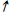 Q and/or
Q and/or P.
P.
B)  M →
M → i → (
i → ( I and/or
I and/or V) → AD →
V) → AD → Q and/or
Q and/or P.
P.
C)  M →
M → V → (
V → ( I and/or
I and/or C) → AD →
C) → AD → Q and/or
Q and/or P.
P.
D)  M →
M → i → (
i → ( I and/or
I and/or C) → AD →
C) → AD → Q and/or
Q and/or P.
P.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q321: When a country finds itself in a
Q322: Expansionary monetary policy is consistent with tightening
Q323: The price of technology stocks collapsed dramatically
Q324: According to the Taylor rule, the more
Q325: Why would an adverse supply shock cause
Q326: One thing all expansionary monetary policies have
Q327: What effect did low interest rates have
Q328: Assuming full employment in the classical model,
Q329: Expansionary monetary policy tends to increase exports.
Q331: Suppose a country faces the following situation: