Multiple Choice
A fatal infectious disease is introduced into a growing population. Let S denote the number of susceptible people at time t and let I denote the number of infected people at time t. Suppose that, in the absence of the disease, the susceptible population grows at a rate proportional to itself, with constant of proportionality 0.2. People in the infected group die at a rate proportional to the infected population with constant of proportionality 0.05. The rate at which people get infected is proportional to the product of the number of susceptibles and the number of infecteds, with constant of proportionality 0.001. Which of the following systems of differential equations are satisfied by S and I?
A) 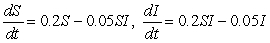
B) 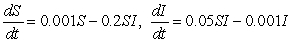
C) 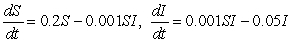
D) 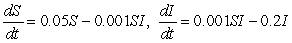
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q47: In a boarding school of 1000 students,
Q48: Newton's Law of Cooling states that the
Q49: A certain bank account earns interest at
Q50: Is <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8190/.jpg" alt="Is a
Q51: Given that <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8190/.jpg" alt="Given that
Q53: On January 1, 1879, records show
Q54: Solve the initial value problem using separation
Q55: There is a theory that says the
Q56: The following figure shows the slope field
Q57: Find the value of k for which