Multiple Choice
A charge is placed on a spherical conductor of radius r1. This sphere is then connected to a distant sphere of radius r2 (not equal to r1) by a conducting wire. After the charges on the spheres are in equilibrium,
A) the electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres are equal.
B) the amount of charge on each sphere is q/2.
C) both spheres are at the same potential.
D) the potentials are in the ratio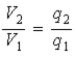 .
.
E) the potentials are in the ratio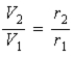 .
.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: Several charges in the neighborhood of point
Q4: The field just outside the surface of
Q5: A series of 3 uncharged concentric shells
Q6: In the Bohr model of the hydrogen
Q7: A charge of 18 nC is uniformly
Q9: Charge of uniform density 90 nC/m<sup>3</sup> is
Q10: Three identical point charges (+2.0 nC) are
Q11: A particle (charge = 50 μC) moves
Q12: A proton (mass = 1.67 × 10−<sup>27</sup>
Q13: The axis of a long hollow metallic