Multiple Choice
Equilibrium: The figure shows two forces acting at right angles on an object. They have magnitudes 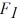 = 6.3 N and
= 6.3 N and 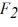 = 2.1 N. What third force will cause the object to be in equilibrium (acceleration equals zero) ?
= 2.1 N. What third force will cause the object to be in equilibrium (acceleration equals zero) ? 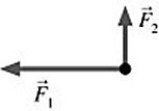
A) 6.6 N at 162° counterclockwise from 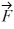
1
B) 6.6 N at 108° counterclockwise from 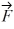
1
C) 4.2 N at 162° counterclockwise from 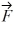
1
D) 4.2 N at 108° counterclockwise from 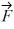
1
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q14: Uniform circular motion: A roadway for stunt
Q15: Slanted surfaces with friction: In the figure,
Q16: Newton's second law: A 60.0-kg person rides
Q17: Uniform circular motion: The figure shows two
Q18: Air resistance: When a parachutist jumps from
Q20: Banked curves: A 600-kg car traveling at
Q21: General questions: You swing a bat and
Q22: Newton's second law: A block is on
Q23: Equilibrium: A woman is straining to lift
Q24: General questions: You are seated in a