Short Answer
Calorimetry: How many grams of ice at - 13°C must be added to 711 grams of water that is initially at a temperature of 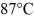 to produce water at a final temperature of
to produce water at a final temperature of 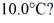 Assume that no heat is lost to the surroundings and that the container has negligible mass. The specific heat of liquid water is 4190 J/kg · °C and of ice is 2050 J/kg · °C. For water the normal melting point is 0.00°C and the heat of fusion is 334 × 103 J/kg. The normal boiling point is 100°C and the heat of vaporization is 2.26 × 106 J/kg.
Assume that no heat is lost to the surroundings and that the container has negligible mass. The specific heat of liquid water is 4190 J/kg · °C and of ice is 2050 J/kg · °C. For water the normal melting point is 0.00°C and the heat of fusion is 334 × 103 J/kg. The normal boiling point is 100°C and the heat of vaporization is 2.26 × 106 J/kg.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: Molecular speeds: A sample of an ideal
Q4: Molecular speeds: Eleven molecules have speeds 16,
Q5: Ideal gas law: The figure shows a
Q6: Molecular speeds: A 5.0-liter gas tank holds
Q7: Thermal expansion: Two identical concrete slabs lie
Q9: Molecular speeds: A container is filled with
Q10: Molecular speeds: A 0.10- <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8274/.jpg" alt="Molecular
Q11: Calorimetry: A person makes ice tea by
Q12: Calorimetry: An 80-g aluminum calorimeter contains 380
Q13: Conduction of heat: Some properties of glass