Short Answer
The restaurant critic on a newspaper claims that the hamburgers that one gets at the hamburger chain restaurants are all equally bad and that people who claim to like one hamburger over others are victims of advertising. In fact, he claims that if there were no differences in appearance, then all hamburgers would be rated equally. To test the critic's assertion, ten teenagers are asked to taste hamburgers from three different fast-food chains. Each hamburger is dressed in the same way (mustard, relish, tomato, and pickle) with the same type of bun. The teenagers taste each hamburger and rate it on a 9-point scale with 1 = bad and 9 = excellent. The data are listed below. 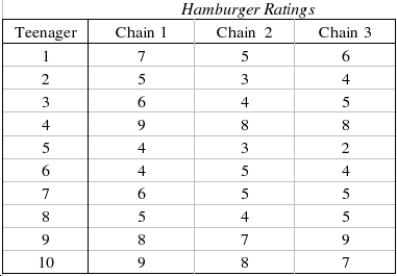 Which statistical technique is appropriate if you want to compare the quality of hamburger of the three chain restaurants?
Which statistical technique is appropriate if you want to compare the quality of hamburger of the three chain restaurants?
______________
Can we infer at the 1% significance level that the critic is wrong?
Test Statistic: ______________
Reject Region:
Reject  if the test statistic > ______________
if the test statistic > ______________
Conclude: ______________
We ______________ infer at the 1% significance level that the critic is wrong.
Using the appropriate statistical table, what statement can be made about the p-value for this test?
______________
Correct Answer:

Verified
Friedman test; 8.667...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q68: The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a nonparametric
Q69: The critical value is taken from the
Q70: In general, before an academic publisher agrees
Q71: The Wilcoxon rank sum test is used
Q72: Which of the following distributions approximate Kruskal-Wallis
Q74: A nonparametric test is one that makes
Q75: Use the Wilcoxon rank sum test on
Q76: Consider the following two independent samples: Sample
Q77: In a Wilcoxon rank sum test for
Q78: A Wilcoxon rank sum test for comparing