Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question.
In order to test how sea urchin sperm bind to eggs, scientists isolated the egg receptor protein that binds to the sperm acrosomal protein called bindin. Plastic beads were coated with egg receptor for bindin (ERB1) from eggs of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, and then the beads mixed with sperm from S. purpuratus or from the related species, S. franciscanus. The researchers counted how many sperm were bound to each bead. The results are shown in the graph below. (Adapted from Kamei and Glabe 2003)
Treatments:
A: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1 beads
B: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with beads containing no ERB1 protein
C: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1 beads
D: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with beads containing no ERB1 protein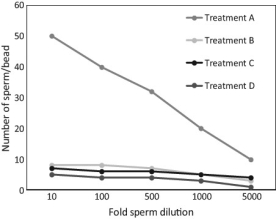
What is a broader implication from the observations of the experiment?
A) In sea urchins, fertilization of eggs by sperm is dependent upon species-specific protein interactions.
B) Only some species of sea urchins use receptor proteins on their eggs to bind sperm.
C) Protein-coated plastic beads should not be used to test sperm binding to eggs.
D) S. franciscanus is probably not a sea urchin, but must be some other type of organism.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q4: The formation of the fertilization envelope requires
Q9: A human blastomere is _.<br>A) an embryonic
Q10: Even in the absence of sperm, metabolic
Q11: Contact of a sea urchin egg with
Q13: Select the choice that correctly matches the
Q14: In humans, identical twins are possible because
Q46: If gastrulation was blocked by an environmental
Q52: The developmental precursors to the gonadal tissues
Q56: The first cavity formed during frog development
Q61: Fertilization of an egg without activation is