Multiple Choice
Producer surplus can be calculated as:
A) 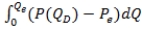 , where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QD) is the inverse demand curve.
, where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QD) is the inverse demand curve.
B) 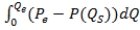 , where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QS) is the inverse supply curve.
, where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QS) is the inverse supply curve.
C) 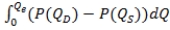 , where Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
, where Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
D) 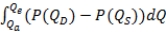 , where Qa denotes actual quantity, Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium, and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
, where Qa denotes actual quantity, Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium, and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q21: If the government subsidizes a product, what
Q22: (Figure: Market for Comic Books I) The
Q23: Many U.S. states have minimum price laws
Q24: Suppose the demand and supply curves for
Q25: All else being equal, a negative supply
Q27: (Figure: Market for Tickets II) As a
Q28: (Figure: Market for Snow Blowers I) Which
Q29: If the government quit subsidizing a product,
Q30: Consumer surplus can be calculated as:<br>A) <img
Q31: (Figure: Market for Tickets II) The size