Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply and the Great Depression 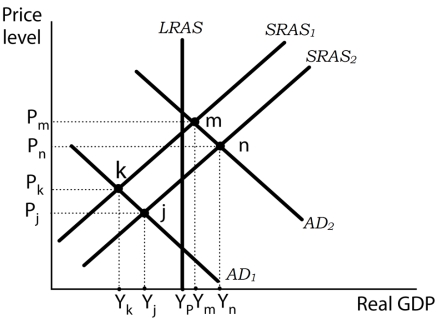
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply and the Great Depression) During the Great Depression, aggregate demand declined sharply, thrusting the economy into a recessionary gap. Nominal wages plunged roughly 20% between 1929 and 1933. How did the economy respond to the falling wages?
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifted left, from SRAS2 to SRAS1, resulting in a short run equilibrium at point k.
B) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifted right, from SRAS1 to SRAS2, resulting in a short run equilibrium at point n.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifted right, from SRAS1 to SRAS2, resulting in a short run equilibrium at point j.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifted left, from SRAS2 to SRAS1, resulting in a short run equilibrium at point m.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q48: Supply-side economics is the belief that fiscal
Q49: Use the following to answer questions.<br>Exhibit: Economic
Q50: Classical economics is based primarily on the
Q50: Which of the following was not an
Q52: Keynesian theory was a response to the
Q54: Which of the following is true about
Q55: In the initial stages of the Great
Q56: Use the following to answer questions.<br>Exhibit: Economic
Q57: David Ricardo focused on the economy in
Q58: Use the following to answer questions .<br>Exhibit: