Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply and the Great Depression 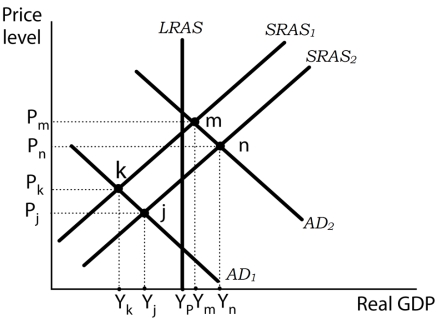
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply and the Great Depression) During the Great Depression, aggregate demand declined sharply. Suppose the economy moved to a short-run equilibrium at point k. Over time, the economy moved to point j. What could have caused the economy to move to point j?
A) Falling output prices caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
B) Falling nominal wages caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
C) Expansionary fiscal policies caused the aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
D) A decline in the demand for U.S. goods by foreign countries aggregate supply to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q37: Milton Friedman was a leader and major
Q101: Which of the following policies would supply-side
Q102: If the economy's short-run aggregate supply curve
Q103: When did policy makers in the U.S.
Q104: Which of the following is true about
Q105: Which of the following statements is true
Q107: Which of the following is true about
Q108: The hypothesis that assumes that individuals form
Q110: During the Great Depression, investment plummeted because<br>A)
Q111: Consider the following statement: "A consistent countercyclical