Short Answer
Phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide or amino acid sequences can be constructed using various algorithms. One simple algorithm is based on a matrix of pairwise genetic distances (divergences) calculated after multiple alignment of the sequences. Imagine you have aligned a particular gene from different hominids (humans and the great apes), and have estimated the normalized number of nucleotide substitutions that have occurred in this gene in each pair of organisms since their divergence from their last common ancestor. You have obtained the following distance matrix.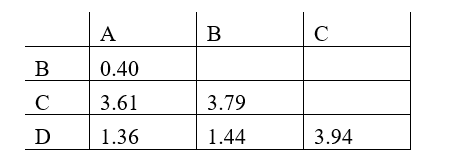
Answer the following question(s) based on this matrix.
-The following tree can be constructed from these distances assuming a constant molecular clock, meaning that the length of each horizontal branch corresponds to evolutionary time as well as to the relative genetic distance from the common ancestor that gave rise to that branch. Indicate which one of the species in the matrix (B to D) corresponds to branches 1 to 3, respectively. Your answer would be a three-letter string composed of letters B, C, and D only, e.g. DCB.
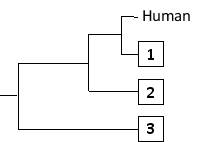
Correct Answer:

Verified
Based on the distances and th...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q11: The two chromosomes in each of the
Q12: In each of the following comparisons, indicate
Q13: Complete the DNA sequence below such that
Q14: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q15: The regions of synteny between the chromosomes
Q17: What are the consequences for the cell
Q18: For the Human Genome Project, cloning of
Q19: A chromatin "reader complex" …<br>A) is always
Q20: A gene that had been turned off
Q21: Which of the following features of DNA