Multiple Choice
After release into the synaptic cleft, the neurotransmitter dopamine is actively taken up by the cells via specific dopamine transporters. The drug cocaine interferes with this process and is therefore called a reuptake inhibitor. The inhibition of the transporter at a certain cocaine concentration is qualitatively represented in the following graph. Based on this graph, which of the following describes the effect of cocaine on the kinetics of dopamine reuptake by the transporter? 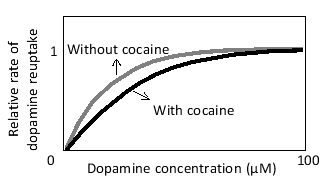
A) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is unaffected, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is reduced.
B) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is reduced, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is unaffected.
C) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is enhanced, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is unaffected.
D) In the presence of cocaine, both the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) and the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine are enhanced.
E) In the presence of cocaine, both the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) and the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine are unaffected, but the transporter is nevertheless inhibited.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q21: Most eukaryotic ABC transporters are involved in
Q22: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the
Q23: A certain neuron in a mouse brain
Q24: Aquaporin has a pair of key asparagine
Q25: The inactivation rate of voltage-gated Na⁺ and
Q27: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q28: An ion channel …<br>A) always mediates passive
Q29: A neuron's repetitive firing rate is limited
Q30: This family of ATPases is structurally related
Q31: A potassium channel conducts K⁺ ions several