Short Answer
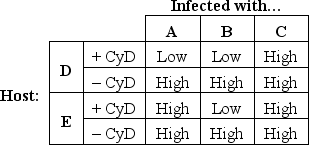
Cytochalasin D (CyD) is a drug that binds to the plus end of actin filaments and prevents actin polymerization. Having identified mutations in actin that confer resistance to CyD, a researcher sets out to study the role of the actin cytoskeleton in the invasion of mammalian host cells by two intracellular parasites: the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and the bacterium Salmonella enterica. She infects wild-type or CyD-resistant host cells with either wild-type T. gondii, CyD-resistant T. gondii, or wild-type S. enterica, each in the presence (+) or absence (-) of CyD, and measures parasite internalization and intracellular proliferation as a result. The findings are summarized in the table below, in which High or Low levels of proliferation are indicated. According to these results, which column (A to C) do you think corresponds to infection with wild-type T. gondii? Which column corresponds to CyD-resistant T. gondii? Which row (D or E) corresponds to the wild-type host? Your answer would be a three-letter string composed of letters A to E only, e.g. ABE.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: How does Helicobacter pylori persist in the
Q2: Modifications of membrane traffic in host cells
Q4: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q5: Mycobacterium tuberculosis can cause tuberculosis, a life-threatening
Q6: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q7: Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular eukaryotic parasite
Q8: Indicate whether the epithelium in each of
Q9: Sort the following events to reflect the
Q10: A point mutation in the gene encoding
Q11: Both Vibrio cholerae and Bacillus anthracis …<br>A)