Multiple Choice
The table shows the marginal-utility schedules for goods A and B for a hypothetical consumer. The price of good A is $1, and the price of good B is $2. The income of the consumer is $8. 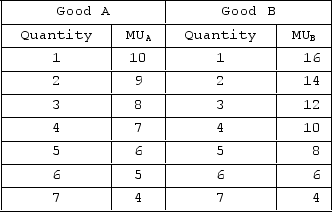 If the price of B falls to $1, while the price of A and the consumer's income stay the same, what would be the utility-maximizing combination of goods A and B?
If the price of B falls to $1, while the price of A and the consumer's income stay the same, what would be the utility-maximizing combination of goods A and B?
A) 5 A and 3 B
B) 4 A and 4 B
C) 3 A and 5 B
D) 2 A and 6 B
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: The first Pepsi yields Craig 18 units
Q2: If a rational consumer is in equilibrium,
Q4: Total utility may be determined by<br>A)multiplying the
Q5: The substitution effect of a price decrease
Q6: Which of the following statements about utility
Q7: If total utility is increasing, then marginal
Q8: An indifference map implies that<br>A)money income is
Q9: All of the following would reduce property
Q10: When a consumer shifts purchases from product
Q11: The table below shows the utility schedule