Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-8 Keynesian aggregate-expenditures model 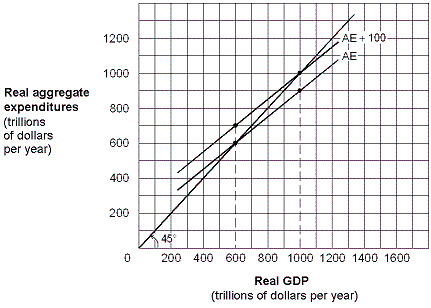 In Exhibit 9-8, an increase in aggregate expenditures causes:
In Exhibit 9-8, an increase in aggregate expenditures causes:
A) a movement down the aggregate demand curve from equilibrium real GDP $600 to equilibrium real GDP $1,000.
B) a movement up the aggregate demand curve from equilibrium real GDP $1,200 to equilibrium real GDP $1,000.
C) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right, causing equilibrium real GDP to increase from $600 to $1,000.
D) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left, causing equilibrium real GDP to decrease from $1,200 to $1,000.
E) no change in equilibrium real GDP.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: In the aggregate expenditures model, equilibrium occurs
Q30: The spending multiplier is:<br>A) 1 / (1
Q52: If the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
Q131: A change in real GDP divided by
Q133: Use the aggregate expenditures model and assume
Q134: Superhighways, public housing facilities, and defense projects
Q135: In the aggregate expenditures model, if an
Q137: Exhibit 9-1 GDP and consumption data <img
Q140: Using the Keynesian aggregate expenditures model, which
Q167: When the MPC gets smaller, the spending