Multiple Choice
Exhibit 6A This is a reaction going on in your muscle cells right this very minute:  The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase catalyzes this reaction in the forward direction as part of the glycolytic pathway. It follows simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics:
The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase catalyzes this reaction in the forward direction as part of the glycolytic pathway. It follows simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics: 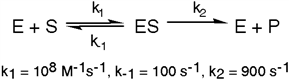
Typical cellular concentrations: triose phosphate isomerase = 0.1 nM
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate = 5 µM glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate = 2 µM
Refer to Exhibit 6A. "Hindrate" is an inhibitor of triose phosphate isomerase. When it is added to cells at a concentration of 0.1 nM, the enzyme's KM for the substrate is unchanged, but the apparent Vmax is altered to 50 nM\sec.
In the following graph, which line best represents the Lineweaver-Burk plot obtained in the presence of hindrate? 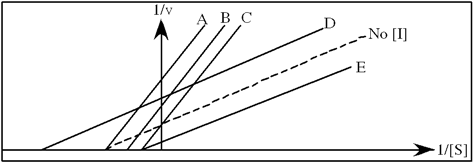
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: The main difference between a catalyzed and
Q3: Which of the following diseases has not
Q4: In the induced-fit model of substrate binding
Q5: Which of the following is true about
Q6: To study the nature of an enzyme,
Q7: The active site of an enzyme<br>A) is
Q8: Which of the following is true about
Q9: The E-S complex often shows as a
Q10: A noncompetitive inhibitor<br>A) binds to the enzyme
Q11: Non-competitive inhibitors have this effect:<br>A) Modifying the