Multiple Choice
Traffic flow. In the analysis of traffic flow, a certain city estimates the following situation for the "square" of its downtown district. In the following figure, the arrows indicate the flow of traffic. If x1 represents the number of cars traveling between intersections A and B, x2 represents the number of cars traveling between B and C, x3 the number between C and D, and x4 the number between D and A, we can formulate equations based on the principle that the number of vehicles entering an intersection equals the number leaving it. That is, for intersection A we obtain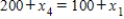
Formulate equations for the traffic at B, C, and D. Solve the system of these four equations.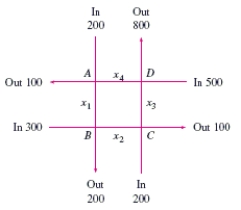
A) 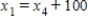 ,
, 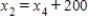 ,
, 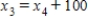 ,
, 
B) 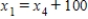 ,
, 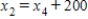 ,
, 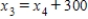 ,
, 
C) 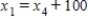 ,
, 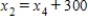 ,
, 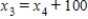 ,
, 
D) 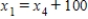 ,
, 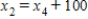 ,
,  ,
, 
E) 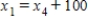 ,
, 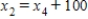 ,
, 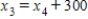 ,
, 
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: Irrigation. An irrigation system allows water to
Q8: Suppose that the U. S. population for
Q9: Use Gaussian elimination method to solve the
Q10: Applying Kirchhoff's Laws to the electrical network
Q11: Solve the following system using either Gaussian
Q13: The given matrix is an augmented matrix
Q14: Solve the system of linear equations. <img
Q15: Suppose that the U. S. population for
Q16: Solve the system of equations by using
Q17: Solve the system of equations by using