Multiple Choice
Let In = 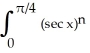 dx. Find a reduction formula for In in terms of In-2 valid for n 3and use it to evaluate I5 =
dx. Find a reduction formula for In in terms of In-2 valid for n 3and use it to evaluate I5 = 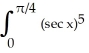 dx.
dx.
A) 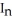 =
= 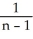
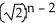 +
+ 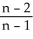
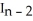 ,
, 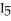 =
= 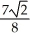 +
+  ln(1 +
ln(1 + 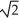 )
)
B) 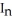 =
= 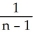
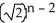 -
- 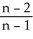
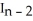 ,
, 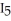 =
= 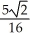 -
-  ln(1 +
ln(1 + 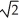 )
)
C) 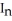 =
= 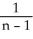
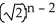 +
+ 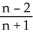
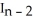 ,
, 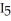 =
= 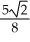 +
+  ln(1 +
ln(1 + 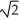 )
)
D) 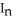 =
= 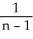
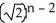 +
+ 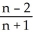
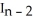 ,
, 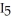 =
= 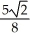 -
-  ln(1 +
ln(1 + 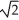 )
)
E) 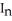 =
= 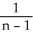
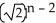 +
+ 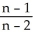
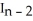 ,
, 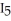 =
= 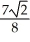 +
+  ln(1 +
ln(1 + 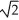 )
)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q93: Integrate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="Integrate dx.
Q94: If g(x) is a polynomial of degree
Q95: Evaluate the integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q96: Determine the exact error involved in approximating
Q97: Use Simpson's Rule with 8 subintervals to
Q99: Evaluate the integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q100: Evaluate the integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q101: Evaluate the integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="
Q102: Evaluate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/.jpg" alt="Evaluate A)
Q103: Calculate the Trapezoid Rule approximations T<sub>2</sub>, T<sub>4</sub>,