Essay
The following figure shows the demand curve for Good X in a perfectly competitive market. Later, the government grants one of the firms the exclusive right to manufacture and sell Good X. MR represents the marginal revenue curve of the firm when it operates as a monopoly. The marginal cost of producing Good X is constant at $5.
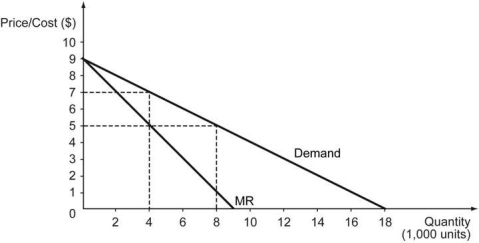 a) What is the quantity supplied when the market is perfectly competitive? What happens to the quantity supplied once the market changes to a monopoly?
a) What is the quantity supplied when the market is perfectly competitive? What happens to the quantity supplied once the market changes to a monopoly?
b) What is the market price when the market is perfectly competitive? What is the market price when the market changes to a monopoly?
c) Compare the consumer surplus when the market is perfectly competitive and the consumer surplus when the market is a monopoly. Is there any producer surplus or deadweight loss in either case? If yes, then how much?
Correct Answer:

Verified
a) A perfectly competitive firm equates ...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q1: Peak-load pricing is when a firm charges
Q2: Country A specializes in the production of
Q3: U.S. Code Title 18 § 1696 states<br>Whoever
Q5: Why do purely technological theories have difficulty
Q6: What makes World's Fair of 1876, in
Q7: The following figure represents the cost and
Q8: Tobac Co. is a monopolist in cigarette
Q9: When a monopolist charges $10 for its
Q10: Firm A is a monopoly because of
Q11: U.S. Code Title 18 § 1696 states<br>Whoever