Multiple Choice
The figure below shows production possibilities curves for tomatoes and oranges in two prefectures in a country.
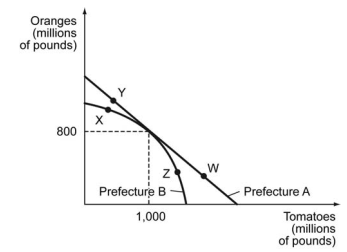
-Refer to the figure above. Suppose that Prefecture A produces at point Y, while Prefecture B produces at point Z. Could there be gains from trade (Prefecture A sells oranges to Prefecture B, and Prefecture B sells tomatoes to Prefecture B) ? Why or why not?
A) Yes, because Prefecture A has a comparative advantage in orange production up to 800 million pounds while Prefecture B has a comparative advantage in tomato production beyond 1 billion pounds.
B) Yes, because Prefecture A produces more oranges while Prefecture B produces more tomatoes.
C) No, because Prefecture A's opportunity cost of producing additional pound of tomatoes at W is higher than Prefecture B's opportunity cost at X.
D) No, because Prefecture A's opportunity cost of producing additional pound of oranges at W is higher than Prefecture B's opportunity cost at X.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: Institutional reversal refers to the fact that
Q4: Suppose an economy produces only solar panels
Q5: The following figure shows the demand curve,
Q6: The following figure depicts the production possibilities
Q7: The following figure depicts the production possibilities
Q9: The following figure depicts the production possibilities
Q10: Yasmin and Zeek are lawyers working at
Q11: The U.S. wheat market is represented by
Q12: Yasmin and Zeek are lawyers working at
Q13: The following figure shows the demand curve,