Essay
Hendricks Ltd. of Calgary manufactures and sells computers. The Manufacturing Division is located in China and transfers 75% of its output to the Assembly Division in the Philippines. The balance of the product is sold in the local market at 2,100 yuan/unit. The Philippines division sells 20% of its output in the local market at 31,500 pesos/unit, with the balance shipped to Calgary. The Calgary operation packages the units and sells the final product at $1,900 Canadian per unit.
The following budget data are available:
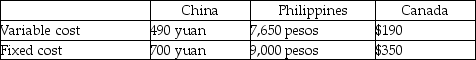
Exchange rates are: $1 Canadian = 7 yuan and $1 Canadian = 45 pesos
Tax rates are 45% in China, 20% in the Philippines and 40% in Canada. Income taxes are not included in the calculation of cost-based transfer prices. Assume that Hendricks does not pay Canadian tax on amounts already taxed in foreign jurisdictions. Take each calculation to 2 decimal places.
Required:
The company has determined that it may transfer units at 250% of variable cost or at market and comply with all existing tax legislation. Which transfer pricing method should the company pursue? Support your recommendation with appropriate calculations.
Correct Answer:

Verified
First translate the foreign currencies i...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q8: Stavanger Ltd. is a Canadian company with
Q9: For each of the following transfer price
Q10: A market is said to be perfectly-competitive
Q11: Sportswear Ltd. manufactures socks. The Athletic Division
Q12: Walton Industries has two divisions: Machining and
Q14: For each of the following transfer price
Q15: The Transportation Division of Petrolia Paint Company
Q16: The Assembly Division of Canadian Car Company
Q17: Sandra's Sheet Metal Company has two divisions.
Q18: A company has two divisions. The Bottle