Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer the questions below:
Two sets of sample data, A and B, are given. Without doing any calculations, indicate in which set of sample data, A or B, there is likely to be stronger evidence of a difference in the population means.
-A scientist performing analysis of variance has the following null hypothesis: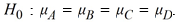
What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis for his analysis?
A) 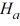 :
: 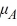
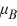
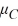
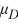 .
.
B) 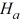 :
: 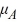 >
> 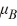 >
> 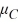 >
> 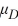 .
.
C) 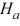 :
: 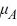 <
< 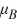 <
< 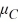 <
< 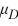 .
.
D) 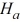 : At least one
: At least one 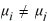
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q32: Use the following to answer the questions
Q33: Use the following to answer the questions
Q34: Use the following to answer the questions
Q35: Use the following to answer the questions
Q36: Use the following to answer the questions
Q38: Use the following to answer the
Q39: Use the following to answer the questions
Q40: Use the following to answer the questions
Q41: Use the following to answer the questions
Q42: Use the following to answer the questions