Multiple Choice
Use the following information when answering the corresponding question(s) .
Suzanne Simard and colleagues knew that the same mycorrhizal fungal species could colonize multiple types of trees.They wondered if the same fungal individual would colonize different trees,forming an underground network that potentially could transport carbon and nutrients from one tree to another (S.Simard et al.1997.Net transfer of carbon between mycorrhizal tree species in the field.Nature 388:579-82) .Figure 31.2 illustrates the team's experimental setup.Pots containing seedlings of three different tree species were set up and grown under natural conditions for three years;two of the three species formed ectomycorrhizae (Douglas fir,birch) and the other (cedar) formed arbuscular mycorrhizae.For the experiment,the researchers placed airtight bags over the Douglas fir and birch seedlings;into each bag,they injected either carbon dioxide made from carbon-13 or carbon-14 (¹³CO₂ and ¹⁴CO₂,isotopes of carbon) .As the seedlings photosynthesized,the radioactive carbon dioxide was converted into radioactively labeled sugars that could be tracked and measured by the researchers.
Figure 31.2
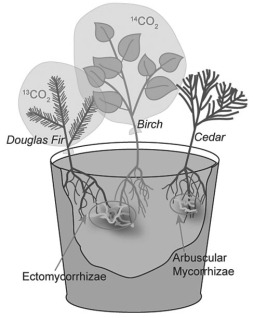
Figure 31.3
-Referring to Simard et al.(1997) ,which design element is the control in this experiment and why?
A) the bags over the seedlings to contain the different types of carbon dioxide
B) the fact that all the seedlings are different species
C) the cedar seedling,because it is not bagged
D) the cedar seedling,because it forms arbuscular mycorrhizae
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q11: Predict what you would see if you
Q21: Basidiomycetes are the only fungal group capable
Q22: Which fungal class is not matched with
Q23: Figure 31.5<br>Use the graphs in Figures 31.4
Q24: It has been hypothesized that fungi and
Q27: A cell has two haploid nuclei.This means
Q28: Many amphibian populations have been decimated by
Q29: Use the following information when answering the
Q34: Fungi that absorb nutrients from decaying plant
Q45: Long, branching fungal filaments are called _.<br>A)