Multiple Choice
Dr. Anderson is a nutritionist who helps clients lose weight prior to surgery. She is working with W. J., a male client who is planning on undergoing a heart transplant. He currently eats more than 3,500 calories a day and has been asked by his doctor to cut the number of calories to about 1,800 (400 for breakfast, 600 for lunch, and 800 for dinner) . She is curious as to whether a food journal will help W. J. reduce the number of calories he eats. A food journal is used to record everything a person eats to help patients be more aware of what they're eating. W. J.'s wife also recorded the food he consumed at each meal to have complete data before introducing the journal. Dr. Anderson decides to phase in the food journal gradually, initially only having W. J. record what he ate at breakfast during the first three days after baseline (days 4-6) . During days 7-9, the journal is used at lunch, too, and during days 10-12, it also is used during dinner. The data for Dr. Anderson's study are below.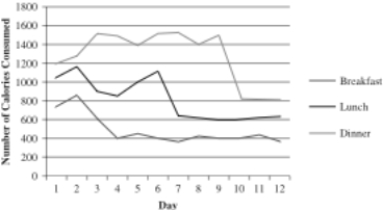
Which of the following is NOT a trade-off of Dr. Anderson's use of a small-N design?
A) She will have limited ability to generalize to other patients.
B) Inferential statistical tests probably cannot be used to examine whether food journals is an effective way to reduce weight.
C) It will be harder to interpret the size of the effect.
D) She will have to use graphs to represent quantitative changes.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q11: Dr. LaGuardia is a cognitive neuroscientist who
Q12: Dr. Fletcher is interested in whether joining
Q13: Layne is trying to watch less television.
Q14: Seeing stability in a stable-baseline design can
Q15: Which of the following is a within-groups
Q17: Dr. Fletcher is interested in understanding whether
Q18: Dr. Fletcher is interested in whether joining
Q19: Which of the following designs has elements
Q20: Layne is trying to watch less television.
Q21: Dr. Anderson is a nutritionist who helps