Multiple Choice
Figure 14.4 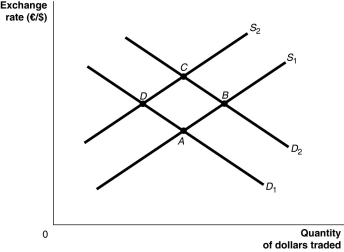 Alt text for Figure 14.4: In figure 14.4, a graph illustrates the quantity of dollars traded against the exchange rate.
Alt text for Figure 14.4: In figure 14.4, a graph illustrates the quantity of dollars traded against the exchange rate.
Long description for Figure 14.4: The x-axis is labelled, quantity of dollars traded, and the y-axis is labelled, exchange rate, euros against dollars.2 supply curves; S1 and S2, and 2 demand curves; D1 and D2 are plotted.Supply curve S1 is a straight line which slopes up from the bottom left corner to the top right corner.It passes through points A and B.Supply curve S2 is a straight line with the same slope as curve S1, but is plotted to the right.Curve S2 passes through points D and C.Demand curve D1 is a straight line which slopes down from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.Curve D1 intersects curve S1 at point A, and curve S2 at point D.Demand curve D2 has the same slope as curve D1, but is plotted to the right Curve D2 intersects curve S1 at point B, and curve S2 at point C.
-Refer to Figure 14.4.Suppose that the Canadian government deficit decreases, causing interest rates in Canada to fall relative to those in the European Union.Assuming all else remains constant, how would this be represented?
A) Supply would decrease, demand would decrease and the economy would move from B to C to D.
B) Supply would increase, demand would decrease and the economy would move from C to B to A.
C) Supply would decrease, demand would increase and the economy would move from A to D to C.
D) Supply would increase, demand would increase and the economy would move from D to A to B.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q56: How does an increase in government purchases
Q92: The current account includes records of a
Q93: If Canadian demand for purchases of Mexican
Q94: How would an increase in the Canadian
Q98: Canada has had negative net exports since
Q99: Ceteris paribus, a real depreciation of the
Q100: When a Canadian investor buys a bond
Q101: Assume Canada is the "domestic" country and
Q120: Currency traders expect the value of the
Q207: How does expansionary monetary policy affect net