Multiple Choice
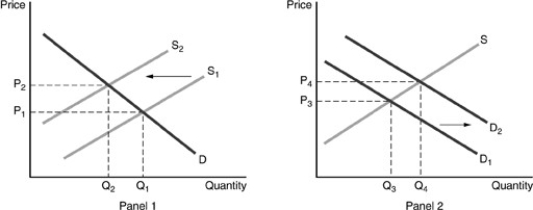 A shift from S1 to S2 reflects the change that happens when a negative externality is taken into account. A shift from D1 to D2 reflects the change that happens when a positive externality is taken into account.
A shift from S1 to S2 reflects the change that happens when a negative externality is taken into account. A shift from D1 to D2 reflects the change that happens when a positive externality is taken into account.
-Refer to the above figures. An external benefit exists. This will lead to a(n)
A) underproduction equal to 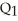 minus
minus 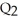 .
.
B) overproduction equal to 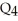 minus
minus 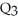 .
.
C) underproduction equal to 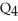 minus
minus 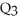 .
.
D) overproduction equal to 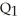 minus
minus 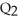 .
.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q26: Government payment of a per-unit subsidy for
Q34: Market failure means that<br>A) the strike organized
Q111: An example of a public good is<br>A)
Q119: Public goods are desired because<br>A) people want
Q223: Over the past 40 years, there has
Q253: The purpose of an effluent fee is
Q267: If a government determines that the provision
Q294: When does a subsidy that benefits consumers
Q295: Consumers are sovereign when<br>A) prices are decided
Q312: One way of addressing the associated market