Multiple Choice
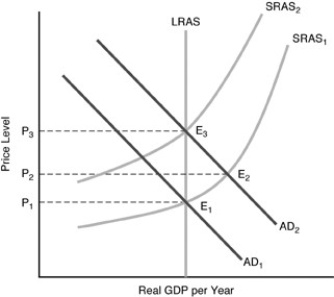
-In the above figure, if we start at 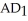 and
and 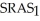 , and the money supply increases unexpectedly, what causes the economy to get to the long-run equilibrium?
, and the money supply increases unexpectedly, what causes the economy to get to the long-run equilibrium?
A) People's expectations will revise after a short-run gain in output, wages will fall, and SRAS will shift leftward.
B) People's expectations will revise after a short-run gain in output, wages will rise, and SRAS will shift rightward.
C) People's expectations will revise after a short-run loss in output, wages will fall, and SRAS will shift leftward.
D) People's expectations will revise after a short-run gain in output, wages will rise, and SRAS will shift leftward.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q31: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5013/.jpg" alt=" -Refer to the
Q33: According to the real business cycle theory,
Q35: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5013/.jpg" alt=" -Suppose the economy
Q128: The Phillips curve shows the relationship between<br>A)the
Q130: Under the rational expectations hypothesis, if wages
Q177: An unexpected decrease in aggregate demand<br>A) causes
Q260: When workers and employers correctly anticipate the
Q265: The idea of policymaking taking place in
Q295: On average, the greater the unexpected decline
Q304: If cyclical unemployment is negative, then<br>A) the