Multiple Choice
Figure 21-17 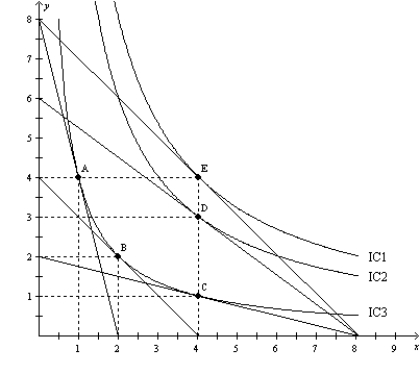
-Refer to Figure 21-17. When the price of X is $40, the price of Y is $40, and income is $160, Paul's optimal choice is point B. Then Paul's income increases to $320, and his optimal choice is point E. For Paul,
A) good X is a normal good, and good Y is an inferior good.
B) good X is an inferior good, and good Y is a normal good.
C) both good X and good Y are normal goods.
D) good Y is a normal good; good X is neither a normal nor an inferior good.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q488: Figure 21-14 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1273/.jpg" alt="Figure 21-14
Q489: Figure 21-13 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1273/.jpg" alt="Figure 21-13
Q490: The consumer's optimum is where<br>A)MU<sub>x</sub>/MU<sub>y</sub> = P<sub>y</sub>/P<sub>x</sub>.<br>B)MU<sub>x</sub>/P<sub>y</sub>
Q491: The two "goods" used when economists analyze
Q492: Figure 21-5<br>(a)<br>(b) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1273/.jpg" alt="Figure 21-5 (a)
Q494: A consumer's preferences for right shoes and
Q495: Which of the following equations corresponds to
Q496: Figure 21-2 The downward-sloping line on the
Q497: Karen, Tara, and Chelsea each buy ice
Q498: Scenario 21-4 Frank spends all of his