Multiple Choice
If a consumer purchases two goods,food (measured along the 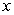 axis) and housing (measured along the
axis) and housing (measured along the 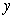 axis) ,then what happens to the slope of the consumer's budget constraint if the price of food falls?
axis) ,then what happens to the slope of the consumer's budget constraint if the price of food falls?
A) The new budget constraint shifts inward but is parallel to the original budget constraint.
B) The new budget constraint pivots inward (towards the origin) along the 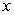 axis. The new slope is steeper than the original slope.
axis. The new slope is steeper than the original slope.
C) The new budget constraint pivots inward (towards the origin) along the 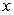 axis. The new slope is flatter than the original slope.
axis. The new slope is flatter than the original slope.
D) The new budget constraint pivots outward (away from the origin) along the 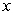 axis. The new slope is flatter than the original slope.
axis. The new slope is flatter than the original slope.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Consumer choice of the basket of goods
Q3: When analyzing how borrowing and lending affect
Q27: Suppose the price of is $20,the price
Q28: Suppose a consumer buys two goods, <img
Q30: If the government would like to induce
Q31: Suppose the price of is $20,the price
Q42: When given a choice between a cash
Q47: If food is on the x-axis and
Q55: Suppose John is planning to join a
Q60: Economists describe consumer choice as a constrained