Multiple Choice
A U.S. FI is raising all of its $20 million liabilities in dollars (one-year CDs) but investing 50 percent in U.S. dollar assets (one-year maturity loans) and 50 percent in U.K. pound sterling assets (one-year maturity loans) . Suppose the promised one-year U.S. CD rate is 9 percent, to be paid in dollars at the end of the year, and that one-year, credit risk-free loans in the United States are yielding only 10 percent. Credit risk-free one-year loans are yielding 16 percent in the United Kingdom. 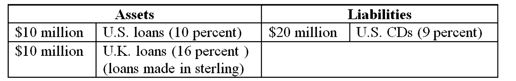
-If the exchange rate had fallen from $1.60/≤1 at the beginning of the year to $1.50/≤1 at the end of the year when the FI needed to repatriate the principal and interest on the loan. What would the dollar loan revenues at the end of the year be as a return on the original dollar investment?
A) 13%.
B) 12.55%.
C) 16%.
D) 8.75%.
E) 7.25%.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q50: A negative net exposure position in FX
Q50: A U.S. bank issues a 1-year, $1
Q51: Assume that instead of investing in Euro
Q53: The decline in European FX volatility during
Q54: The reason an FI receives a fee
Q59: The following are the net currency
Q60: The decrease in European FX volatility during
Q74: The FI is acting as a hedger
Q91: If foreign currency exchange rates are highly
Q105: The total FX risk for a domestic