Multiple Choice
Which one of the following equations represents the ionization of a weak monoprotic acid in water?
A) HCN(aq) + H2O(l) 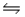 H3O+(aq) + CN-(aq)
H3O+(aq) + CN-(aq)
B) HCN(aq) + OH-(aq) 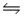 H2O(l) + CN+(aq)
H2O(l) + CN+(aq)
C) CN- (aq) + H2O(aq) 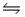 HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
D) HCN(aq) + OH- (aq) 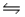 H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
E) HCN(aq) + NH3(aq) 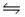 NH4CN(aq)
NH4CN(aq)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q15: What is the pH of a
Q27: Which one of the following salts will
Q51: The hydrolysis of NH<sub>4</sub>F will result in
Q73: HCN is classified as a weak acid
Q74: Calculate the concentration of chromate ion (CrO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>)in
Q76: The OH<sup>-</sup> concentration in a 2.5 ×
Q79: Al(OH)<sub>3</sub> is an amphoteric hydroxide.Write a balanced
Q80: Given the following K<sub>a</sub> values, which anion
Q82: Write the formula for the conjugate base
Q113: A 5.5 L sample of a 0.25