Multiple Choice
Does a water molecule become more or less polar when bound to a metal ion, such as 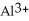 ? Why? (Hint: How might the electrons of the O-H covalent bonds in water "feel" about the highly charged aluminum ion?)
? Why? (Hint: How might the electrons of the O-H covalent bonds in water "feel" about the highly charged aluminum ion?)
A) Less polar. Aluminum ion is so highly polar that it attracts the electrons in a water molecule to itself and away from the oxygen atom in water, causing water to lose polar character.
B) More polar. The electrons in the O-H bond are drawn even closer to the oxygen (and away from the hydrogen) as they are drawn towards the positive charge of the aluminum ion.
C) Neither. Although polarity may increase as a water molecule approaches an aluminum ion, once the water molecule becomes bound to the metal ion its polarity reverts to its original status.
D) Both. As a first water molecule approaches 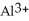 , there is an increase in water's polarity. However, the "bond" becomes less polar when the aluminum ion has captured all six water molecules to form
, there is an increase in water's polarity. However, the "bond" becomes less polar when the aluminum ion has captured all six water molecules to form 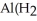 O
O 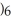 3+.
3+.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Which of the following solutions is the
Q22: What is a base?<br>A)anything that accepts a
Q60: When the pH of a solution is
Q63: At what point will a buffer solution
Q64: When the hydronium ion concentration equals 10
Q69: Can an acid and a base react
Q82: If the pH of a solution is
Q97: Which of the following statements is not
Q120: For the following acid-base reaction,identify what compound
Q164: What is the main characteristic of a