Multiple Choice
For the log-log model ln(y) = β0 + β1ln(x) + ε, the predicted value of y is computed as ________.
A)  = b0 + b1x
= b0 + b1x
B)  = exp(b0 + b1ln(x) +
= exp(b0 + b1ln(x) + 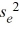 /2)
/2)
C)  = b0 + b1ln(x)
= b0 + b1ln(x)
D)  = exp(b0 + b1x +
= exp(b0 + b1x + 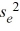 /2)
/2)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q78: Which of the following regression models is
Q79: The log-log and the _ models can
Q80: It is believed that the sales volume
Q81: The following data show the demand for
Q82: Which of the following is a typical
Q84: A cubic regression model is a polynomial
Q85: The coefficient of determination R<sup>2</sup> cannot be
Q86: When the predicted value of the response
Q87: Typically, the sales volume declines with an
Q88: The following data show the demand for