Multiple Choice
A researcher wants to study the effects of physical exercise on depression.She randomly selects a group of 24 individuals who are equally depressed.None of these individuals currently exercises.She then randomly assigns them in one of three groups: group 1 stays without exercising (sedentary group) ,group 2 exercises once a week,and group 3 exercises two times a week.Individuals in groups 2 and 3 meet with a personal trainer so they carry out a very similar exercising program,both in kinds of exercises and in intensity.After two months,the researcher has all individuals take a depression-assessment test.The score of the test goes from 0 = totally miserable to 100 = complete satisfaction. The scores are shown in the following table: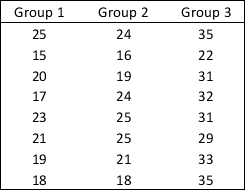 The researcher uses a Kruskal-Wallis test and a significance level α = 0.05.The appropriate decision is ______.
The researcher uses a Kruskal-Wallis test and a significance level α = 0.05.The appropriate decision is ______.
A) fail to reject the null hypothesis that the three groups have different levels of depression
B) reject the null hypothesis that the three groups have different levels of depression
C) fail to reject the null hypothesis that the three groups have equal levels of depression
D) reject the null hypothesis that the three groups have equal levels of depression
E) fail to reject the null hypothesis that the sample is random
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q14: Nonparametric statistics are sometimes called distribution-dependent statistics.
Q20: The nonparametric alternative to linear regression is
Q22: The nonparametric counterpart of the t test
Q58: A quality control supervisor wishes to determine
Q60: In the one-sample runs test for randomness
Q61: A quality control supervisor wishes to determine
Q64: A local pediatrician office is interested in
Q89: Which of the following tests should be
Q103: Prior to computing a Friedman test, the
Q109: Statistical techniques based on fewer assumptions about