Multiple Choice
Biologists hypothesize that the protein collagen is both a structural ingredient in bone and a stimulating molecule that induces immature bone cells to develop and produce other ingredients for bone growth.To test this hypothesis, two groups of mice were studied from birth to adulthood.One mouse group was normal, while the other carried a mutation in a gene that controls the synthesis of type I collagen.Panel A in the figure below compares the sizes of the mice in the two groups, and panel B compares their weights.Panel C compares the skeletal features of the two groups, with dark gray representing bone and light gray representing cartilage. 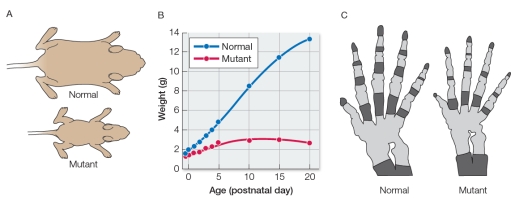 Which statement can be made about the nature of the mutation in the experimental group?
Which statement can be made about the nature of the mutation in the experimental group?
A) The mutation prevents type I collagen synthesis.
B) The mutation significantly slows type I collagen synthesis.
C) The mutation significantly stimulates type I collagen synthesis.
D) The mutation delays the initiation of type I collagen synthesis until late in development.
E) The mutation initiates type I collagen synthesis much earlier than normal.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q33: Organisms in Archaea and Bacteria do not
Q34: In what way do mitochondrial membranes differ
Q35: The _ is a cell structure with
Q36: How might a researcher study the presence
Q37: Researchers have used several pieces of evidence
Q39: If you removed the pili from a
Q40: Refer to the figure below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q41: Tough ropelike filaments that stabilize cell structure
Q42: In some prokaryotic organisms, the plasma membrane
Q43: Some organelles in eukaryotic cells are thought