Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure and table below. 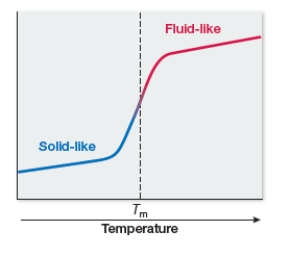
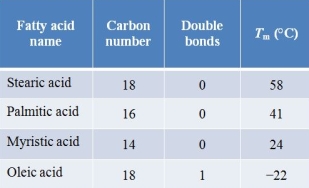 At low temperatures, cell membranes become quite immobile and solid-like.If the temperature is gradually increased, a membrane undergoes small changes until a large change in fluidity is observed.The midpoint temperature corresponding to this large change is called the melting temperature.The graph shows how a cell membrane's melting temperature (Tm) is measured.The table shows melting temperature data collected from membranes composed of phospholipids containing different fatty acids.Which statement is consistent with these data?
At low temperatures, cell membranes become quite immobile and solid-like.If the temperature is gradually increased, a membrane undergoes small changes until a large change in fluidity is observed.The midpoint temperature corresponding to this large change is called the melting temperature.The graph shows how a cell membrane's melting temperature (Tm) is measured.The table shows melting temperature data collected from membranes composed of phospholipids containing different fatty acids.Which statement is consistent with these data?
A) Increasing chain length or introducing double bonds into fatty acids in membrane phospholipids increases temperature-dependent membrane fluidity.
B) Increasing chain length or omitting double bonds from fatty acids in membrane phospholipids increases temperature-dependent membrane fluidity.
C) Decreasing chain length or introducing double bonds into fatty acids in membrane phospholipids increases temperature-dependent membrane fluidity.
D) Decreasing chain length of fatty acids in membrane phospholipids increases membrane fluidity, but introducing double bonds has no effect on temperature-dependent membrane fluidity.
E) Increasing chain length of fatty acids in membrane phospholipids increases temperature-dependent membrane fluidity, but introducing double bonds has no effect on fluidity.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q213: White blood cells can defend the body
Q214: A researcher studying a line of mouse
Q215: Refer to the figure below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q216: Refer to the figure below showing the
Q217: You are working in a lab that
Q219: If a red blood cell with an
Q220: A marathon runner has just arrived in
Q221: Refer to the figure below showing a
Q222: If a cell needs to acquire cholesterol,
Q223: Refer to the table below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"