Multiple Choice
Refer to the figures below. 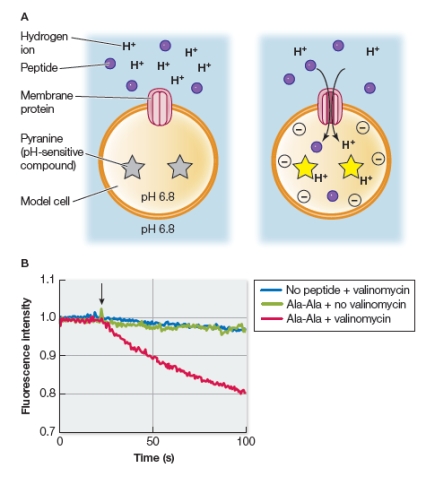 Researchers investigating the uptake of dipeptides by bacterial cells constructed model cells by embedding the membrane protein responsible for peptide transport in a lipid bilayer.They loaded the interior of the model cell with potassium ions and pyranine, a fluorescent molecule that undergoes a decrease in its fluorescence intensity at low pH.The researchers used the small molecule valinomycin to interact with the membrane lipids of the model cell to release potassium ions into the surrounding environment (no membrane protein is needed for this release) .Upon doing this, the researchers observed an almost immediate change in fluorescence of the pyranine still inside the model cells, but only under certain conditions, as detailed in the graph.What do the results shown in the graph suggest about the membrane protein?
Researchers investigating the uptake of dipeptides by bacterial cells constructed model cells by embedding the membrane protein responsible for peptide transport in a lipid bilayer.They loaded the interior of the model cell with potassium ions and pyranine, a fluorescent molecule that undergoes a decrease in its fluorescence intensity at low pH.The researchers used the small molecule valinomycin to interact with the membrane lipids of the model cell to release potassium ions into the surrounding environment (no membrane protein is needed for this release) .Upon doing this, the researchers observed an almost immediate change in fluorescence of the pyranine still inside the model cells, but only under certain conditions, as detailed in the graph.What do the results shown in the graph suggest about the membrane protein?
A) The membrane protein is a uniporter that transports dipeptides against their concentration gradients.
B) The membrane protein is a symporter that transports dipeptides only at the same time it transports hydrogen ions.
C) The membrane protein is a symporter that transports dipeptides only at the same time it transports potassium ions.
D) The membrane protein is an antiporter that transports dipeptides in exchange for hydrogen ions.
E) The membrane protein is an antiporter that transports dipeptides in exchange for potassium ions.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q32: In animal cells, tight junctions and desmosomes
Q33: Refer to the figure below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q34: Protein movement within a membrane may be
Q35: Refer to the graphs below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q36: The plasma membrane of the bacterium Pseudomonas
Q38: Osmosis is a specific form of<br>A) diffusion.<br>B)
Q39: Which is not involved in secondary active
Q40: A barrier to the rapid movement of
Q41: Transporters that move two substances at once
Q42: All of the following affect the rate