Multiple Choice
While traveling the galaxy in a spacecraft,you and a colleague set out to investigate the 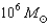 black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?
black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?
A) His/her signals,because he/she is orbiting well outside the event horizon that lies 0.02 AU from the black hole.
B) His/her signals,but shifted to a much redder wavelength because he/she is close to the event horizon that lies 0.8 AU from the black hole.
C) Nothing,because your colleague has crossed the event horizon that lies 8 AU from the black hole.
D) Nothing,because no light can escape the gravitational pull of a black hole no matter how close he/she is to it.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: With the Hubble Space Telescope,you discover a
Q3: Light is increasingly redshifted near a black
Q4: The event horizon of a black hole
Q5: An iron core cannot support a massive
Q8: Which of the following is NOT a
Q9: You observed three different star clusters and
Q10: As a high-mass main-sequence star evolves off
Q11: Using the Hubble Space Telescope,you discover a
Q15: High-mass stars differ from low-mass stars in
Q90: Galileo supposedly experimented with gravity by dropping