Multiple Choice
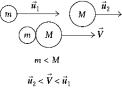 A ball of mass m and velocity
A ball of mass m and velocity 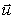 1 collides with and sticks to a ball of mass M and velocity
1 collides with and sticks to a ball of mass M and velocity 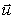 2. If the pair moves on with velocity
2. If the pair moves on with velocity 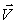 , the impulse given the ball of mass m during the collision must have been
, the impulse given the ball of mass m during the collision must have been
A) m( 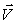 -
- 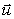 1)
1)
B) m( 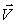 +
+ 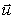 1)
1)
C) (m + M) 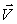
D) (m + M) ( 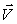 -
- 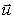 2)
2)
E) zero
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q20: A particle of unknown mass has a
Q38: For a system consisting of two particles
Q40: The SI units of momentum are<br>A)kg ·
Q71: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/.jpg" alt=" The figure shows
Q73: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/.jpg" alt=" Two identical bodies
Q77: In a coordinate system whose center of
Q78: Use the scenario below for the
Q79: Calculate the impulse by the force, as
Q90: A block that has a mass M
Q91: In an elastic collision of two objects,<br>A)momentum