Multiple Choice
A tool manufacturer tests three types of cutters used in a lathe operation. One type is a laminated steel cutter made of very hard high-carbon steel sandwiched between two softer steels. Another is a special high-speed steel cutter developed using powder metallurgy. The final one is made from cryogenically treated steel. Cutters of each type are tested to see how long they will last (in hours) in continuous operation until they need to be sharpened. The times are recorded for each cutter used in the study, and the results are given below. 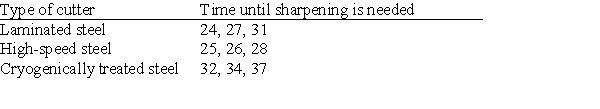 The data are to be analyzed with the Kruskal-Wallis test. The null hypothesis is that the time until sharpening is needed has the same distribution in all groups. The alternative is:
The data are to be analyzed with the Kruskal-Wallis test. The null hypothesis is that the time until sharpening is needed has the same distribution in all groups. The alternative is:
A) mean time until sharpening is needed is systematically higher in some groups than others.
B) not all three mean times until sharpening is needed are equal.
C) the mean times until sharpening are different in each of the three groups of cutter type.
D) the times until sharpening is needed are systematically longer for cryogenically treated steel cutters than for the other two types of cutters.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q18: The primary difference between the null hypothesis
Q19: The use of carpeting in hospitals, while
Q20: Fifteen stores were selected to test the
Q21: The use of carpeting in hospitals, while
Q22: Which of the following is part of
Q23: The Wilcoxon rank sum test for comparing
Q24: In a study to investigate the effect
Q25: Which of the following is false?<br>A)As the
Q26: In a study to investigate the effect
Q28: The alternative hypothesis for the Kruskal-Wallis test